The VIX Volatility Index
What you'll learn
What the VIX is, how it’s calculated, and what it represents
How the VIX reacts to market movements and investor sentiment
Ways to trade the VIX: futures, options, ETFs (like VXX, UVXY), and CFDs
How to use the VIX to hedge against market downturns
Trading strategies based on volatility spikes and mean reversion
Solana Trading For Beginners
What you'll learn
What Solana is and how it compares to other major blockchains
The basics of trading SOL on popular crypto exchanges
How to analyze SOL’s price using technical and fundamental indicators
How to place your first trade and manage risk effectively
Common beginner mistakes and how to avoid them
What is Dogecoin
What you'll learn
What Dogecoin is, how it originated, and what drives its price
How Dogecoin differs from other major cryptocurrencies
The basics of CFD trading and how it applies to DOGE
Advantages and risks of trading Dogecoin CFDs vs. spot trading
How to use technical analysis, leverage, and stop-losses in CFD trades
How to trade Ethereum
What you'll learn
The basics of Ethereum and how it differs from other cryptocurrencies
How to analyze Ethereum’s price using technical and fundamental tools
Different ways to trade Ethereum (spot, margin, futures, and options)
How to choose a trading platform and manage risk effectively
Practical trading strategies for trending, ranging, and volatile markets
What is Ripple (XRP)?
What you'll learn
What Ripple and XRP are, and how they differ
How the Ripple network facilitates cross-border payments
The role of XRP as a bridge currency in financial transactions
Key differences between XRP and other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum
Regulatory considerations and the current state of Ripple in global markets
Crypto Trading
What you'll learn
In the Crypto Education Course, learners will discover the foundations of cryptocurrency trading and investing. The course explains how blockchain technology works, introduces major digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and demonstrates how crypto markets differ from traditional markets. Participants will learn how to open and manage a crypto trading account, understand market charts, use trading platforms, and practice risk management tailored to the volatility of crypto assets. By the end, beginners will have the knowledge to approach cryptocurrency trading with confidence and make informed decisions in this fast-growing sector.
What is Litecoin
What you'll learn
What Litecoin is, how it works, and its use cases
Key differences between Litecoin and other major cryptocurrencies
How to trade Litecoin on spot, margin, and CFD markets
Technical and fundamental tools for analyzing LTC price movements
Risk management strategies and trading tips specific to LTC
Economic Indicators
What you'll learn
What economic indicators are and why they matter in financial markets
The difference between leading, lagging, and coincident indicators
Key indicators to watch (e.g., GDP, CPI, NFP, interest rates, PMI)
How economic data impacts currencies, stocks, bonds, and commodities
How to use economic calendars and plan around news releases
Most Traded Cryptocurrencies Globally
What you'll learn
Overview of the top traded cryptocurrencies by volume and market cap
The technology, use cases, and teams behind leading coins like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others
How liquidity and volatility affect trading opportunities
Key metrics for analyzing and comparing different cryptocurrencies
How to build a diversified crypto trading or investment strategy
Trading an IPO
What you'll learn
What an IPO is and how the IPO process works
How to analyze a company before it goes public
Key factors that influence IPO price movement
Trading strategies for IPO day and post-IPO opportunities
Risks and challenges unique to IPO trading
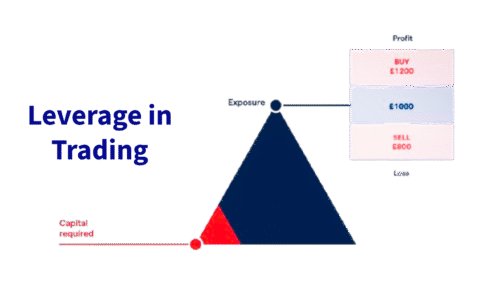
Leverage in Trading
What you'll learn
What leverage is and how it works in different markets
The relationship between leverage, margin, and position size
How to calculate leveraged trades and potential outcomes
Risks of over-leveraging and how to avoid common mistakes
How to use leverage responsibly within your trading strategy
Understanding Pips
What you'll learn
What a pip is and how it differs across currency pairs (standard, JPY pairs, etc.)
How to calculate pip value based on trade size and currency pair
How pip value affects profit, loss, and risk management in forex trades
The difference between pip value, tick size, and point value in other markets
How to use a pip value calculator and apply it to position sizing
Trade the Non-Farm Payrolls
What you'll learn
What the NFP report is, how it's calculated, and why it moves markets
How to interpret NFP data alongside unemployment rate and average hourly earnings
Pre-release strategies: how to prepare using forecasts, sentiment, and positioning
Live trading strategies for high-volatility conditions (breakouts, fades, traps)
Post-release analysis and how to adjust your trading plan based on the results
Consumer Price Index
What you'll learn
What the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is and how it measures inflation
Why CPI is closely watched by central banks like the Federal Reserve and ECB
How CPI data impacts markets such as forex (USD pairs), gold, indices, and bonds
Pre-release analysis techniques, consensus expectations, and market positioning
Trading strategies for before, during, and after CPI announcements, including volatility setups
Hang Seng Index
What you'll learn
The composition and structure of the Hang Seng Index and how it reflects the Hong Kong economy
Key economic, political, and sector-specific drivers of HSI price movements
How to analyze Hang Seng Index charts using technical indicators and price action
Trading strategies specific to the HSI, including momentum, breakout, and reversal setups
How to manage risk and position sizing when trading this highly volatile index
Cotton Futures
What you'll learn
The structure and specifications of cotton futures contracts, including tick size, contract size, and expiry
Key drivers of cotton prices, including global supply and demand, weather, and trade policies
How producers, manufacturers, and traders use cotton futures to hedge price risk
Techniques for applying technical and fundamental analysis to cotton markets
Trading strategies tailored to the volatility and seasonality of soft commodities like cotton
Cocoa Futures
What you'll learn
The fundamentals of cocoa futures contracts, including contract size, tick value, and delivery months
Key price drivers such as crop yields, political risk in producing countries, and global demand
How to use cocoa futures for hedging, speculation, or long-term investment strategies
Methods for conducting technical and fundamental analysis specific to soft commodities
Strategies for navigating the unique volatility and seasonality of cocoa markets
Coffee Futures
What you'll learn
The structure of coffee futures contracts (Arabica vs. Robusta), including lot size, tick value, and settlement
Key factors driving global coffee prices, such as weather, origin risk, and demand cycles
How commercial players (growers, roasters, importers) use coffee futures for hedging
How to apply technical and fundamental analysis to soft commodity markets
Effective trading strategies for volatile and seasonally-driven markets like coffee
Wheat Futures
What you'll learn
The basics of wheat futures contracts, including tick size, margin requirements, and contract expiration
Key market fundamentals affecting wheat prices: weather, harvest cycles, global supply, and trade flows
How producers and traders use wheat futures for hedging and price risk management
Techniques for analyzing wheat markets using both technical and fundamental tools
Practical trading strategies tailored to the unique characteristics of the wheat market
Soybean Futures
What you'll learn
The structure and mechanics of soybean futures contracts, including tick size, margin, and expiration
Major market drivers affecting soybean prices, such as weather, global trade, and crop reports
How to use soybean futures for hedging, risk management, and portfolio diversification
Techniques for technical and fundamental analysis specific to agricultural markets
Practical strategies for trading soybean futures, from short-term setups to long-term positioning
Corn Futures
What you'll learn
The fundamentals of corn futures and how they are traded on exchanges like CBOT
Key factors that influence corn prices, including supply, demand, weather, and global markets
How to read and interpret a corn futures contract (contract size, tick value, expiration dates)
Risk management strategies using corn futures, including hedging and stop-loss techniques
How to analyze market trends and apply technical and fundamental analysis in corn futures trading
What is xStation
What you'll learn
How to navigate the xStation platform and customize your trading workspace
How to place, manage, and close trades using different order types
How to analyze charts using technical indicators and drawing tools
How to use built-in tools like the trading calculator and risk management settings
How to access and apply real-time news, market sentiment, and heatmaps in your trading decisions
Introduction to Livestock
What you'll learn
Livestock Futures – Live Cattle
Live Cattle futures are designed to allow feedlot operators to hedge against a decline in price before they are able to sell the cattle for processing, and for buyers, such as meat packers, to manage the risk of an increase in the price of the cattle they are planning to purchase for processing, or to protect their profit margin for beef they have committed to ship in the future.
Live Cattle futures trade in units of 40,000 pounds and in minimum price increments of $10.00. They are listed for trading in the even months of February, April, June, August, October and December. Live Cattle is a physically-delivered futures contract, meaning that live steers are ultimately delivered. There are specific standards in terms of the quantity and USDA grade of cattle that can be delivered. The details on the delivery requirements and procedures for Live Cattle futures can be found in the CME Rulebook on the CME Group website.
Lean Hogs
Lean Hogs refers to a hog that is ready for processing at about 275 pounds. Hogs are mainly produced in the Midwest, and it typically takes about six months for a pig to become market-ready. The carcass of a market hog weighs about 200 pounds and will typically yield about 155 pounds of lean meat, which is the core of the lean hog futures contract.
Lean Hog futures allow sellers and buyers, such hog producers and packers, to manage the risk of adverse price movements in their operations. Lean Hog futures trade in units of 40,000 pounds of hog carcasses and in minimum price increments of $10.00. They are listed in February, April, May, June, July, August, October and December. As with Feeder Cattle, Lean Hog futures are settled in cash at expiration, to at a price equal to the CME Lean Hog Index on the last day of trading.
Introduction to Trading Stocks
What you'll learn
Key Takeaways from the Trading Stocks Course
Understand Stock Market Basics – Learn what stocks are, how stock exchanges function, and the role of brokers and regulators.
Different Trading Styles – Explore approaches such as day trading, swing trading, and position trading, and identify which fits your goals.
Reading Charts & Indicators – Gain the ability to analyze stock charts, recognize patterns, and apply technical indicators for informed decisions.
Fundamental Analysis – Discover how to evaluate company performance using earnings, balance sheets, and market news.
Risk & Money Management – Learn essential strategies for managing risk, setting stop-losses, and protecting your trading capital.
Market Psychology – Understand trader behavior, emotions, and how market sentiment influences stock prices.
Building a Trading Plan – Create a structured, disciplined approach to trading that supports long-term growth.
Hands-on Learning – Apply knowledge through practice examples, simulated trades, and real market scenarios.
Introduction to CFD’s
What you'll learn
In the CFD Trading course, students will learn how to approach financial markets using Contracts for Difference as a flexible tool for trading. They will gain a clear understanding of how CFDs work, including leverage, margin, and the mechanics of going long or short. The course introduces essential trading strategies and risk management techniques, helping students balance opportunities with potential risks. Learners will also explore how to analyze markets through both technical and fundamental methods, practice identifying entry and exit points, and understand the costs associated with CFD trading. By the end, students will be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to start practicing CFD trading in demo environments and prepare for live market participation.
Introduction to Trading Styles
What you'll learn
In this section, students will explore the different trading styles that define how market participants approach decision-making and manage timeframes. You will learn the distinctions between scalping, day trading, swing trading, and position trading, and understand how each style requires unique levels of time commitment, risk management, and strategy. The course will also highlight the psychological and lifestyle factors that influence which trading style may be most suitable for you, helping you match your personal goals, temperament, and availability with an effective trading approach. By the end, you will be able to identify which style aligns with your objectives and how to adapt your techniques as market conditions change.